If a scale of 10 kg can distinguish 1 g of weight change, then the main components of this scale are often incremental accumulators. When designers need temperature measurements with an accuracy of 0.01 degrees, incrementally accumulating ADCs are often the preferred solution. The delta-sigma ADC can also replace the traditional successive approximation register ADCs with a gain stage. Because these data converters are ideal for measuring small changes in the real world, precision instruments such as temperature sensors, balances, transducers, flow meters, and countless other types of sensors are ideal for incrementally accumulating ADCs.
The incremental accumulation of the ADC may seem complicated on the surface, but in reality it is an accurate data converter consisting of a series of simple components. The incremental accumulation ADC consists of two main components: an incremental accumulation modulator that performs analog-to-digital conversion and a digital low-pass filter/decimation circuit. The basic building blocks of the incremental accumulation modulator (integrated operational amplifier, summing node, comparator / 1-bit ADC, and 1-bit DAC) are shown in Figure 1. The modulator's charge balancing circuit forces the digital output bit stream of the comparator to represent the average analog input signal. While the comparator output is sent back to the modulator's 1-bit DAC, it is also processed using a low-pass digital filter. This filter mainly calculates the number of 0s and 1 and removes a lot of noise, thus implementing a data converter of up to 24 bits.
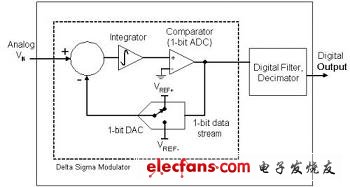
Figure 1: Incremental Accumulation ADC consists of an incremental accumulator that performs analog-to-digital conversion followed by a digital filter and decimator
One of the main obstacles to achieving more digit resolution is noise. For designers who are trying to discern microvolt (μV) level changes from thermocouples, sensors or other low-level sources, noise will be a major problem. The noise floor consists of the sum of the noise generated by all unwanted external and noise sources around the modulator. And the thicker the noise floor, the harder it is to detect the actual change in the analog input signal you are trying to test.
Oversampling, noise shaping, digital filtering, and decimation are four important methods used by incremental accumulators to reduce noise and produce high-resolution output data. Assuming that the input signal of a data converter is sampled at frequency fS, fS must be at least twice the input frequency (fIN = fS/2) according to the Nyquist theorem of the data. Oversampling samples the input signal at a frequency that is more than twice the frequency of the input signal. A larger oversampling ratio (k) will result in a more adequate digital bitstream representation. The more "1" or "0" that make up the bit stream, the better the numerical approximation of the input signal. Figure 2 shows how oversampling at a sample rate of kx fS/2 allows the modulator to spread the same amount of noise over a wider range of frequencies. This greatly reduces the noise floor in the frequency band of interest. For every 2 times increase in oversampling rate, the ideal signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is increased by 3dB. A larger SNR means that the incremental accumulation converter can better distinguish smaller changes in the analog input.
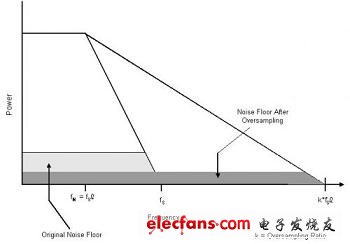
Figure 2: Oversampling reduces the noise floor in the band of interest
The incremental summation converter accurately measures the analog input by performing noise shaping with an integrator in the modulator control loop. The noise shaping process of the integrator is to force more noise to a higher frequency, as shown in Figure 3. The digital low pass filter then removes the high frequency portion of the noise, which greatly improves the SNR. Digital filters can also be used to greatly reduce noise at 50Hz, 60Hz or other unwanted frequencies.
Evaporative Air Cooler is a new kind of cooling machine which can save more energy but also has strong cooling ability. With ice box and cooling pad, the air cooler can make your room temperature lower and lower. It is widely used in hotels, restaurants, supermarkets and factories.
Our well-equipped facilities and excellent quality control throughout all stages of production enable us to guarantee total customer satisfaction. Besides, we have received CE, CB, RoHS and CCC certifications.
As a result of our high quality products and outstanding customer service, we have gained a global sales network reaching America, Asia, Europe, Africa, the Middle East and other countries and regions.
If you are interested in any of our products or would like to discuss a custom order, please feel free to contact us. We are looking forward to forming successful business relationships with new clients around the world in the near future.
Evaporative Air Cooler
Room Air Cooler,Water Air Cooler,Arctic Air Cooler,Air Water Cooler
Ningbo Banshen Electric Appliance Co., Ltd , https://www.banshendq.com
